這篇繼續擴充訂單功能,可以回顧一下先前畫的架構圖,我們要有一張中間的表來記錄購物車內有哪些商品資訊,這部分建立訂單可以想像完成選擇要購買的商品之後送出訂單所產生的資料紀錄。
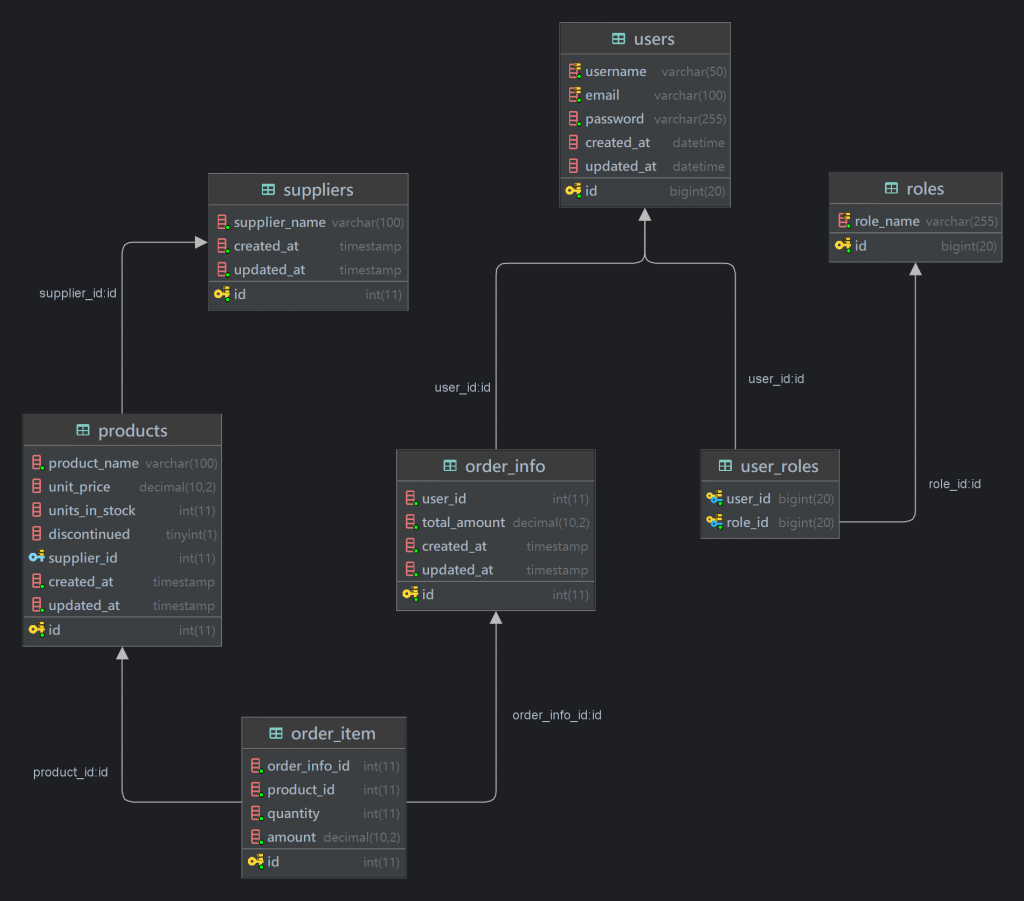
order_info 訂單資訊,用來記錄我們整筆訂單的彙整資訊,包含關聯哪位 user, 總金額多少
order_item 訂單項目資訊,用來記錄整筆訂單中各別項目關聯哪個 product (product_id)、購買數量是多少(quantity)、價錢(amount),從中也可以知道屬於哪筆訂單(order_info_id)。
CREATE TABLE order_info
(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
user_id INT NOT NULL,
total_amount DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL, -- 訂單總花費
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
);
CREATE TABLE order_item
(
id INT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
order_info_id INT NOT NULL,
product_id INT NOT NULL,
quantity INT NOT NULL,
amount DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL
);
Entity
// OrderInfo.class
@Entity
@Data
@Table(name = "order_info")
public class OrderInfo extends BaseEntity {
private Integer userId;
private Double totalAmount;
}
// OrderItem.class
@Entity
@Data
@Table(name = "order_item")
public class OrderItem {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer id;
private Integer orderInfoId;
private Integer productId;
private Integer quantity;
private Double amount;
}
DTO (CreateOrderInfoRequest.class, CreateOrderResponse.class)
// 建立訂單請求
@Data
public class CreateOrderInfoRequest {
@NotEmpty
private List<BuyItem> buyItemList;
}
// 回傳建立訂單
@Data
public class CreateOrderResponse {
private OrderInfo orderInfo;
private List<HashMap<String, Object>> orderItemList;
}
當勾選好要哪些商品要送出訂單時就會呼叫這隻 API 建立訂單
Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class OrderInfoController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderInfoController.class);
@Autowired
private OrderService orderService;
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping("/users/{userId}/orders")
public ResponseEntity<?> createOrder(@PathVariable Integer userId,
@RequestBody @Valid CreateOrderInfoRequest createOrderInfoRequest) {
Optional<User> user = userService.getUserByID(userId);
if (!user.isPresent()) {
log.warn("UserId: {} is not found", userId);
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
CreateOrderResponse createOrderResponse = orderService.createOrder(userId, createOrderInfoRequest);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body(createOrderResponse);
}
}
Service
這邊 createOrder 的運作流程:
@Service
public class OrderService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OrderService.class);
@Autowired
private OrderInfoDao orderInfoDao;
@Autowired
private OrderItemDao orderItemDao;
@Autowired
private ProductDao productDao;
@Transactional
public CreateOrderResponse createOrder(Integer userId, CreateOrderInfoRequest createOrderInfoRequest) {
Double totalAmount = 0.0;
List<OrderItem> orderItemList = new ArrayList<>();
for (BuyItem buyItem : createOrderInfoRequest.getBuyItemList()) {
Product product = productDao.findById(buyItem.getProductId())
.orElseThrow(() -> {
log.warn("productId: {} not found", buyItem.getProductId());
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
});
if (product.getUnitsInStock() < buyItem.getQuantity()) {
log.warn("productId: {} stock is not enough, remaining stock is {}, requested quantity is {}", buyItem.getProductId(), product.getUnitsInStock(), buyItem.getQuantity());
throw new ResponseStatusException(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST);
}
// 計算價錢
double amount = (buyItem.getQuantity() * product.getUnitPrice());
totalAmount += amount;
OrderItem orderItem = new OrderItem();
orderItem.setProductId(buyItem.getProductId());
orderItem.setQuantity(buyItem.getQuantity());
orderItem.setAmount(amount);
// 扣庫存
int updateStock = product.getUnitsInStock() - orderItem.getQuantity();
product.setUnitsInStock(updateStock);
productDao.save(product);
orderItemList.add(orderItem);
}
// 存 orderInfo
OrderInfo orderInfo = new OrderInfo();
orderInfo.setUserId(userId);
orderInfo.setTotalAmount(totalAmount);
OrderInfo orderInfoSaved = orderInfoDao.save(orderInfo);
int orderInfoId = orderInfoSaved.getId();
// 存多筆 orderItem
orderItemList.forEach(item -> item.setOrderInfoId(orderInfoId));
orderItemDao.saveAll(orderItemList);
// response
List<HashMap<String, Object>> responseOrderItemList = new ArrayList<>();
for (OrderItem orderItem : orderItemList) {
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Product product = productDao.findById(orderItem.getProductId()).get();
map.put("orderItemId", orderItem.getId());
map.put("orderInfoId", orderItem.getOrderInfoId());
map.put("productId", orderItem.getProductId());
map.put("quantity", orderItem.getQuantity());
map.put("amount", orderItem.getAmount());
map.put("productName", product.getProductName());
responseOrderItemList.add(map);
}
CreateOrderResponse createOrderResponse = new CreateOrderResponse();
createOrderResponse.setOrderInfo(orderInfoSaved);
createOrderResponse.setOrderItemList(responseOrderItemList);
return createOrderResponse;
}
}
dao
public interface OrderInfoDao extends JpaRepository<OrderInfo, Integer> {
}
public interface OrderItemDao extends JpaRepository<OrderItem, Integer> {
}
這邊希望可以針對特定路徑 (/api/users/{userId}/orders )去判斷,只有自己能夠建立自己訂單如果創建訂單 userId 沒有對應路徑上的 userId 就會不給與權限。
針對 SecurityConfig 設置,有特別的寫法可以讓進行請求時進入特定方法來驗證,這邊加上一個 checkUserIdAndRole 方法,裡面用到 Authentication 物件來確認登入者資訊,因為登入取得 JWT 後,這些資訊就會存入 Security Context ,讓你可以取出來進行驗證。
我這邊有特別開放讓 Admin 可以不受限制建立所有路徑下的訂單,主要是要設計讓 ROLE_BUYER 才可以針對自己路徑的訂單建立,符合 Restful 的風格。
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity httpSecurity) throws Exception {
return httpSecurity
.csrf(customizer -> customizer.disable())
.authorizeHttpRequests((registry) -> registry
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/register", "/login").permitAll()
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/error", "/api/products/**").permitAll()
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/checkAuthentication").hasAnyAuthority("ROLE_BUYER", "ROLE_SELLER", "ROLE_ADMIN")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/api/products").hasAuthority("ROLE_SELLER")
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.DELETE, "/api/products").hasAuthority("ROLE_SELLER")
.requestMatchers("/api/users/*").hasAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN")
// 透過 checkUserIdAndRole 來確認權限
.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST, "/api/users/{userId}/orders").access(this::checkUserIdAndRole)
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.sessionManagement(session -> session.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS))
.addFilterBefore(jwtFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.build();
}
private AuthorizationDecision checkUserIdAndRole(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, RequestAuthorizationContext context) {
int userId = Integer.parseInt(context.getVariables().get("userId"));
Authentication auth = authentication.get();
// 轉型問題處理
if (!(auth.getPrincipal() instanceof UserPrincipal userPrincipal)) {
return new AuthorizationDecision(false);
}
boolean hasAccess = auth.getAuthorities().stream()
.anyMatch(a -> a.getAuthority().equals("ROLE_ADMIN")) ||
// 當前 userId 對應路徑 userId 才允許授權
(auth.getAuthorities().stream().anyMatch(a -> a.getAuthority().equals("ROLE_BUYER")) && userPrincipal.getId().equals(userId));
log.info("checkUserIdAndRole access permit: {}", hasAccess);
return new AuthorizationDecision(hasAccess);
}
以上大致就完成建立訂單的創建跟權限設定。
{
"buyItemList": [
{
"productId": 1,
"quantity":1
},
{
"productId": 2,
"quantity":1
}
]
}
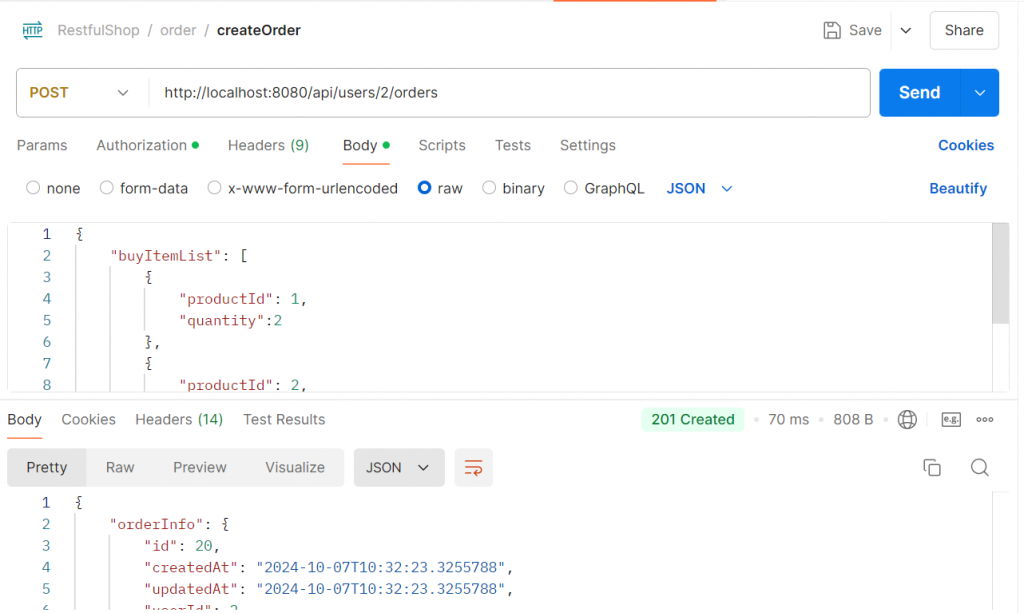
對應其 id = 2路徑就可以創建
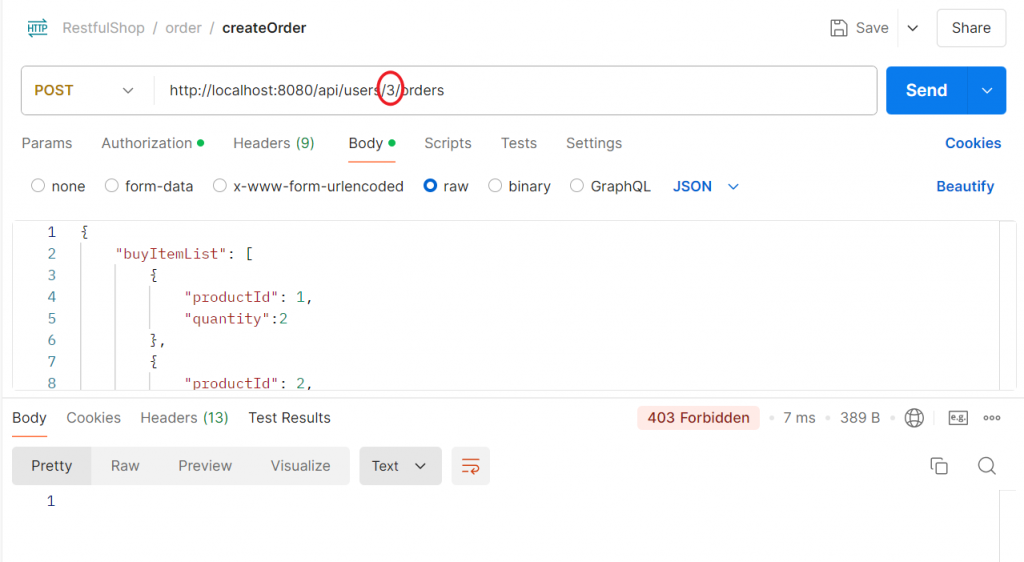
如果用其他 id 路徑就會被禁止
以上大概是這次介紹這些電商的一些功能設計,還有加入 Security 權限控管的一些實作,實際上還有很多東西都可以細部去設計,這邊提供一些實務上的應用給大家參考。
下一篇就簡單寫一些測試也應用到之前的介紹,讓大家可以比較了解應用 Spring Boot 實務的開發部分。
相關文章也會同步更新我的部落格,有興趣也可以在裡面找其他的技術分享跟資訊。
